PV column
energy
2025/10/01
“Soaring global demand drives upgrades in energy storage duration and cell specification” by InfoLink
Energy Storage Systems (ESS) are gaining attention in Japan as grid storage systems, and their adoption is more advanced around the world than in Japan, contributing to the use of grids and the further spread of renewable energy.
In this column, we will introduce the current status of energy storage systems around the world through a report published on September 18, 2025 by InfoLink Consulting, a Taiwanese research and consulting company on renewable energy and technology, titled “Soaring global demand drives upgrades in energy storage duration and cell specification.“
**********
Soaring global demand drives upgrades in energy storage duration and cell specification
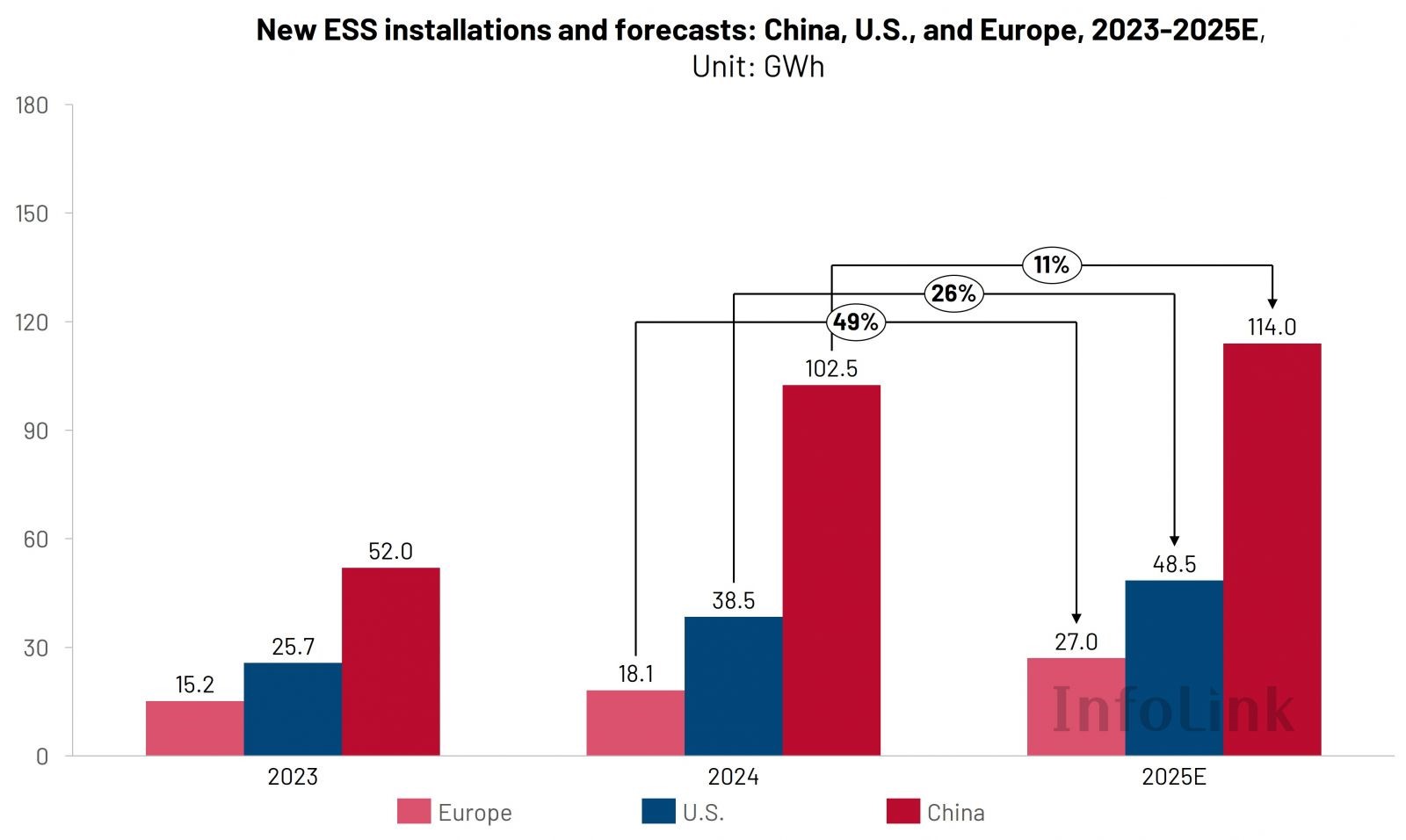
Global ESS demand continues to rise, with new installations expected to exceed 230 GWh in 2025
Since 2024, the role of electrochemical energy storage has shifted from being an “add-on” to the power system to a “necessary configuration.” Rising renewable penetration, limited grid flexibility, electricity price volatility, and interconnection constraints have transformed energy storage from a supporting role into a system hub — tasked with not only peak shaving and frequency regulation but also ensuring grid capacity and resilience.
Looking ahead to 2025–2030, the global electrochemical energy storage market is expected to remain highly prosperous, with the U.S., China, and Europe entering a period of concentrated growth. Two-hour and four-hour energy storage systems (ESS) will coexist, driven by installations on both the grid side and the renewables side. If capacity remuneration and the Long Duration Energy Storage (LDES) mechanisms are implemented more quickly, combined with further declines in ESS and cell prices, installation growth could accelerate further, with new installations in 2025 likely to exceed 230 GWh.
China’s market is shifting from being “policy-driven” to “dual-driven by policy and market.” Wind/solar-plus-storage projects are entering a stage of “flexible normalization,” while more detailed rules for capacity remuneration and ancillary service settlement are making storage revenues increasingly “measurable and bankable.” In addition, convergence of manufacturing and system integration is further reducing lifetime costs and shortening delivery cycles. Three key triggers are likely to drive market transformation over the next two years: the rollout of provincial capacity remuneration and settlement rules, accelerated growth of four-hour projects in regions with high curtailment, and the entry of shared and stand-alone storage into the power market. On the C&I side, driven by time-of-use (TOU) and demand charges, the penetration of 200–300 kWh all-in-one systems is likely to increase rapidly.。
The European market is transitioning from a focus on ensuring energy security and system resilience to pursuing market-based returns. Uncertain gas supply alongside high renewable penetration is elevating the role of energy storage in capacity provision, emergency supply, and inertia replacement. Capacity mechanisms and LDES pilots rolled out in countries such as the UK and Italy are supporting project financing and long-term revenues, while more favorable trading and dispatch rules—including finer time resolution and the expansion of balancing and frequency regulation markets—are creating greater opportunities for revenue optimization. Over the next two years, market growth is expected to be driven jointly by successive rounds of capacity market rollouts, the implementation of LDES policies, growing preference for 4–6h projects due to higher capacity value, and accelerated permitting and interconnection processes that shorten the “development-to-operation” cycle.
For the following two to three years, the U.S. market will be characterized by “policy support, regional expansion, and deeper commercialization.” Federal tax incentives—such as the investment tax credits (ITC)–together with state-level programs will continue to play a major role, with four-hour durations dominating utility-scale projects, and demand expanding beyond California and Texas to a broader range of states. Interconnection processes and market rules are steadily improving, enabling projects to capture multiple value streams across energy, ancillary services, and capacity markets. On the financing side, growing preference for standardized designs, mature supply chains, and long-term contracts is enhancing bankability and delivery certainty.
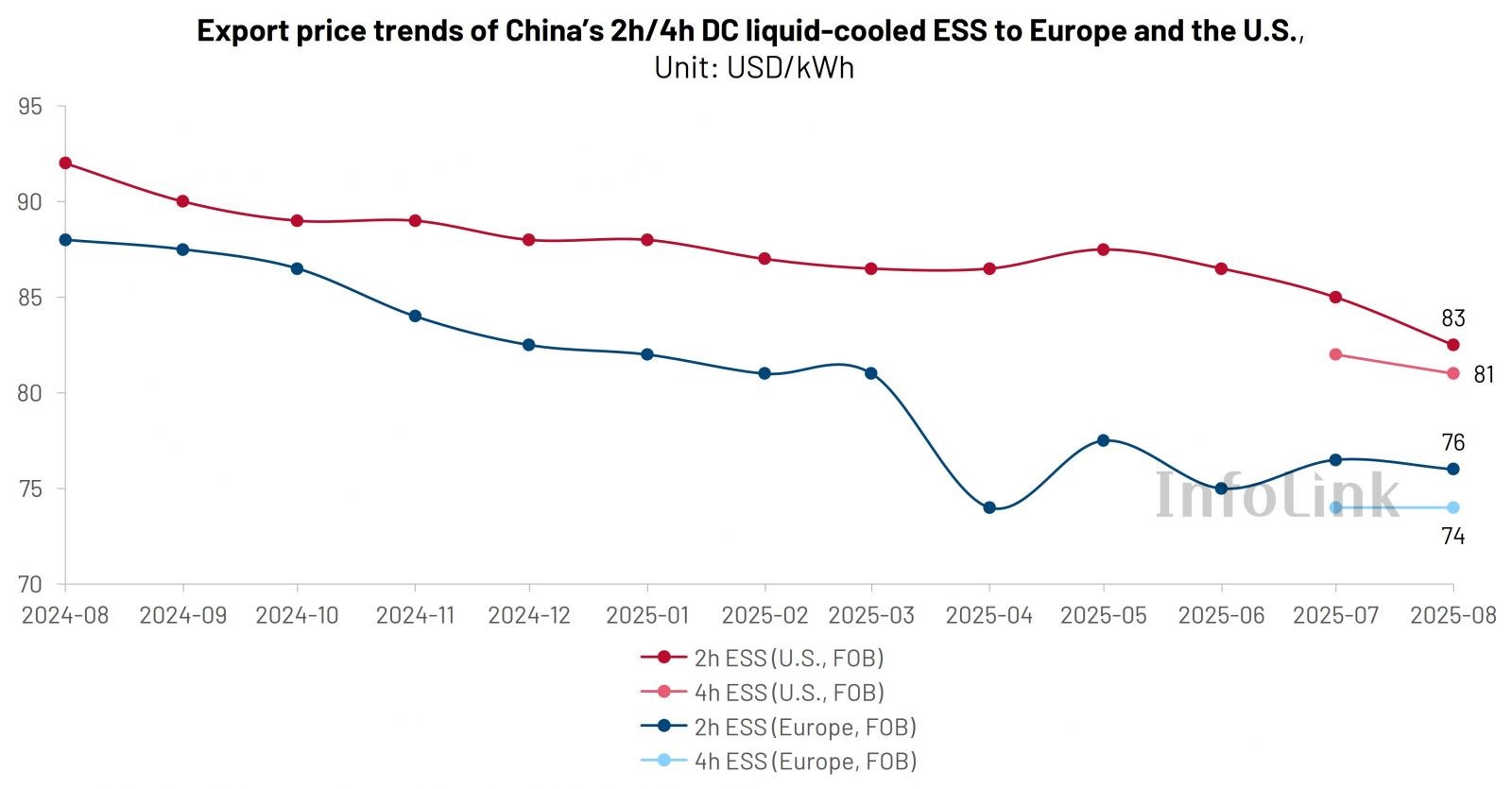
4-hour ESS gain traction
With better unit energy cost economics and clear advantages in long-duration buffering and sustained load regulation scenarios, adoption of 4-hour and longer-duration ESS is increasing in certain countries and regions.
4h ESS has largely become a mainstream option. In California, where the grid is operated by the California Independent System Operator (CAISO), utility-scale battery energy storage systems (BESS) are predominantly 4h. In the Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO) market, capacity accreditation rules give higher value to 4h systems, encouraging developers to adopt them as the preferred option for new projects. Similarly, in Texas, where the grid is operated by the Electric Reliability Council of Texas (ERCOT), project durations are rapidly shifting from 1–2h to 2–4h.
In Europe, existing projects are still dominated by 1–2h systems, though the average duration is trending upward. In Spain, multiple tenders and subsidy programs explicitly require or prioritize ≥4h systems, while Italy’s capacity mechanism—including the Meccanismo di Asta per la Capacità di Stoccaggio di Energia (MACSE, Energy Storage Capacity Allocation Mechanism)—is also driving 4h toward the mainstream. The UK has already shifted rapidly from 1h to ≥2h, with the share of 4h projects steadily increasing.
Overall, the U.S. will maintain 4h as the mainstream duration in 2025–2026, Europe will remain on an upward trajectory from 1–2h to 2–4h, and Southern Europe will serve as the key driver for accelerating 4h penetration.
InfoLink adds 4h ESS price tracking, reflecting rapid evolution of mainstream durations.
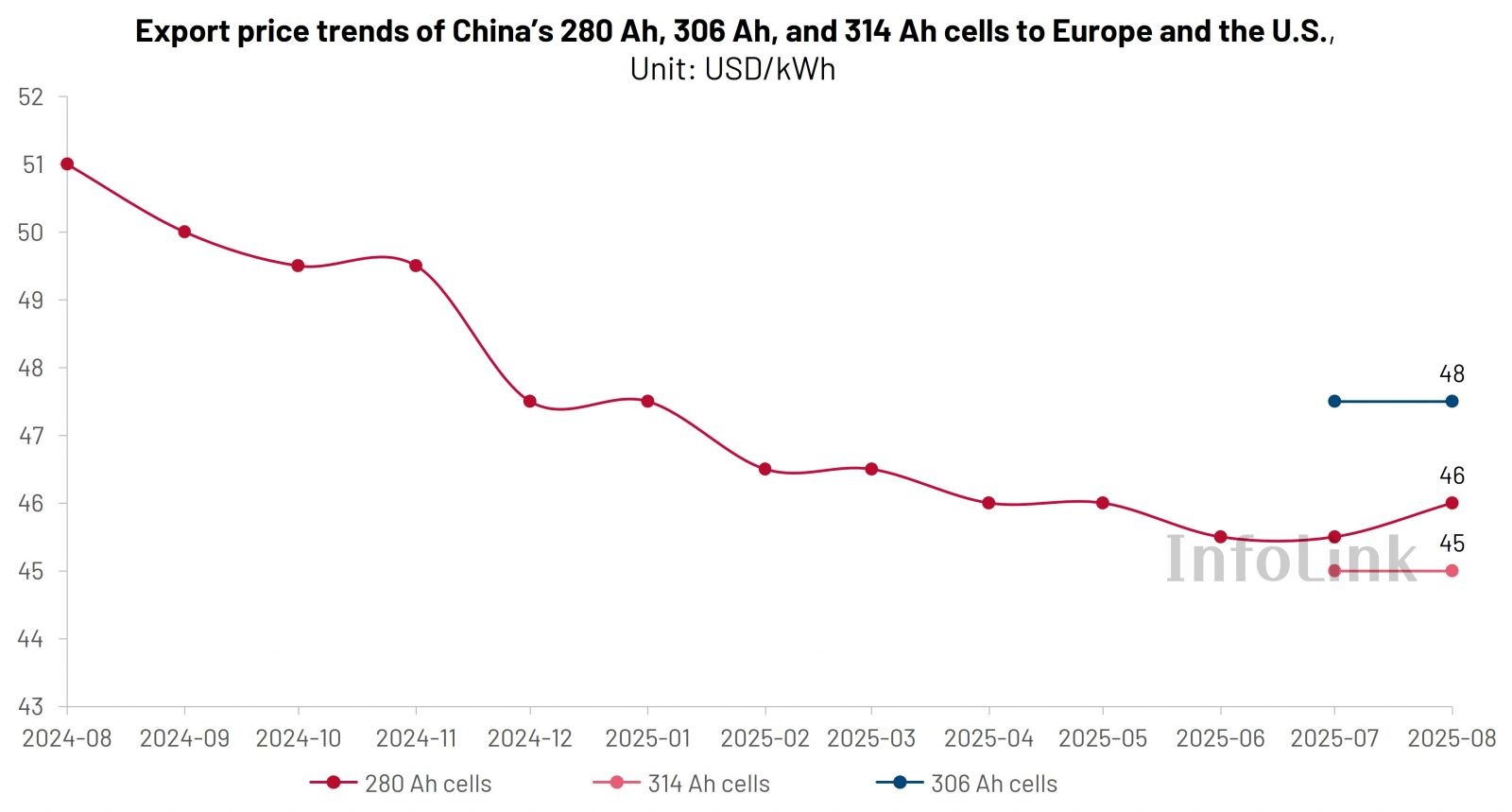
4h ESS drives cell specifications trends: 300+ Ah becomes mainstream
In 4h ESS applications, project revenues rely more heavily on unit energy cost and usable energy. Increasing cell capacity (Ah) and container energy density can help reduce the levelized cost of storage (LCOS) and improve bankability. As a result, utility-scale storage cell specifications are shifting from 280 Ah toward 300+ Ah, with 314 Ah expected to achieve significant penetration in 2025.
In the U.S., 4h has become the common configuration. Combined with compliance and localization requirements, the proven 314 Ah cell is more easily scaled up for deployment, while the 306 Ah cell is mainly used to serve existing platform demand or for compatibility replacements.
In Europe, driven by ≥4h tenders and capacity mechanisms, projects increasingly favor energy-oriented solutions with higher Ah, and new projects generally lean toward 314 Ah. Meanwhile, due to considerations of platform compatibility, thermal management redundancy, and safety margins per unit capacity, demand for 306 Ah remains significant in transitional projects and retrofit applications. The practical value of 306 Ah includes the following:
- Enabling smooth upgrades under existing container and battery management system (BMS) conditions, reducing retrofit complexity and downtime;
- Delivering better overall cost-performance in scenarios requiring lower C-rates, higher cycle life, or sensitivity to upfront investment; and,
- Forming a “primary–backup specification” combination with 314 Ah, which enhances multi-supplier coordination and spare parts interoperability, thereby improving supply chain resilience and O&M maintainability.
InfoLink expands report coverage to include 306 Ah and 314 Ah cell price tracking in non-China markets, helping clients gain insights into market iteration and price trends.
**********
As with this article, foreign media often features case studies, policies, systems, and technologies from China, Europe, and the United States, but unfortunately, no examples from Japan. Also, while 10 years ago, energy storage (battery) was considered Japan’s specialty, unfortunately, such comments are no longer seen even in Japan.
In terms of infrastructure configuration and electricity bill reduction, countries around the world are making daily improvements in the introduction of renewable energy and energy storage systems, as well as policies, and manufacturers are facing global competition.
It is unfortunate that Japan is currently being left behind by the rest of the world, but we would like to contribute to creating examples from Japan that attract global attention.
Acknowledgments: We would like to thank InfoLink Consulting, Taiwan, for introducing us to this useful article.

